CRM
Low Impact Development (LID)
Green infrastructure and low-impact development are planning approaches to increase nature-based solutions to reduce urban heat islands, capture and treat stormwater on-site, reduce water use, and restore natural hydrology, improving water quality, decreasing flooding, and helping communities thrive.
Most backyards and open spaces are suitable to capture rainfall, reducing outdoor water demand, and making a low-impact development both functional and appealing. Outdoor water use can be substantial, and expensive, but property owners can easily reduce or eliminate external water use and save money:
Click here For more on stormwater management.
Sample student projects, below, have advanced green infrastructure.
Most backyards and open spaces are suitable to capture rainfall, reducing outdoor water demand, and making a low-impact development both functional and appealing. Outdoor water use can be substantial, and expensive, but property owners can easily reduce or eliminate external water use and save money:
- Water your lawn at dawn or dusk, when more water soaks in than during the hottest parts of the day.
- Plant native flowers and shrubs and seed your lawn with drought tolerant turf grass.
- Retain moisture in your lawn and garden by using compost mulching around your plants.
- Install rain water barrels under the roof gutter drains and use this rain water to water your plants.
- Reduce lawn size- less lawn means less watering and less mowing, replacing lawn with garden beds, trees, and meadows, all of which also support beneficial wildlife habitat.
- Adjust your mower to a high setting and leave grass clippings and chopped-up leaves on the lawn to increase soil organic material.
- Use porous hardscapes on paths and patios to allow rain water to pass into the soil.
- Water lawn less to increase plants’ tolerance to drought.
- Make a rain garden (click here) to hold rainfall runoff or stormwater and improve water quality. Rain gardens create beautiful landscapes, filter pollutants, and enhance wildlife habitat.
Click here For more on stormwater management.
Sample student projects, below, have advanced green infrastructure.
|
This project analyzed Boston Harbor Islands National Park viewsheds, and the cultural, historical, and natural features that influence public perceptions. The study used a modified version of the Bureau of Land Management’s Visual Resource Management tool to assess the unique island landscapes. Visual assessment through a quantitative analytical process, calibrated with an expert panel of stakeholders, resulted in recommendations to help the National Park Service increase visitor’s access to underused areas and incorporate landscape management plans to maintain the scenic viewsheds.
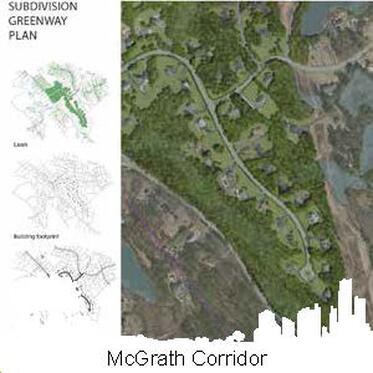
The McGrath Highway Green Infrastructure graduate studio proposed transforming this elevated Somerville, MA highway into a green infrastructure corridor. Students presented the City of Somerville with three scenarios. The Gray scenario focuses on short term solutions, such as reducing the number of vehicle drive lanes and replacing them with trees. The green scenario focuses on the long term goals for social and environmental issues and to promote economic development by lowering the elevated portion of the McGrath Highway and creating a boulevard. The super green scenario proposed transforming the elevated portion of the highway into a green pedestrian corridor.
|
|
The Ipswich River, has relatively low pollution levels, is an important source of drinking water for over 300,000 people, and is a key part of the rich Great Marsh ecosystem. The river is, however, one of the most threatened rivers in the United States, with development pressures, drinking water withdrawals, and occasionally extremely low summer flows.
A UMass studio proposed a green infrastructure plan for the watershed, protecting open space an wildlife habitat and creating recreational linkages. Projects include retrofitting neighborhoods with rain gardens and other green infrastructure devices to gather and treat urban stormwater, creating ecological corridors and green infrastructure retrofits. |
|
This senior undergraduate landscape architecture studio, in partnership with Groundworks Lawrence, designed greenways for the historic industrial city of Lawrence, MA. Students compiled five alternative into a greenway plan:
Legacy Greenway to create connections between important assets, Regional Lawrence to improve regional connectivity, Merrimac River to create greenway loops that connect to the three rivers, Rail Trail-Merrimac River to create connecting corridors, and Spicket River to connect people back to the river by engaging them in history. |
|
This green infrastructure graduate studio explored creating green infrastructure networks in Worcester, Massachusetts, in conjunction with the EcoTarium. The studio project builds on the City’s open space plan goals by planning improved access to water resources, increased connectivity and wayfinding between existing parks and open space, and safer bicycle and pedestrian connections. The project also strives to improve water quality in the Blackstone River and reduce stormwater runoff by a series of green infrastructure improvements throughout the City.
|
|
The senior undergraduate landscape architecture studio developed a conceptual greenway plan for the Town of Framingham. The plan explores how to connect diverse neighborhoods, schools, jobs, retail centers, natural, cultural, and recreational resources through a network of pedestrian and bike trails, building on Framingham’s Open Space and Recreation Plan.
|
Copyright © 2024